CANCER AWARENESS
Blood Cancer Awareness
Blood cancers encompass a group of malignancies that affect the blood, bone marrow, lymph nodes, and other tissues. The three main types of blood cancers are leukemia, lymphoma, and plasma cell neoplasm.
Leukemia is defined as acute myeloid leukemia (AML), myeloid sarcoma, myeloproliferative neoplasms such as chronic myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic neoplasm, yelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm, mastocytosis, and histiocytic/dendritic neoplasms. Lymphoma is defined as mature B-cell neoplasms, which include many B-cell lymphomas from small B-cell lymphomas to large B-cell lymphomas, such as small lymphocytic leukemia/lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, etc.; precursor B-cell neoplasms such as B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma; Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), which includes classic Hodgkin lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte predominance Hodgkin lymphoma; and peripheral T-cell Lymphomas such as precursor T-cell neoplasms, T-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma, mature T-cell and NK-cell leukaemia/lymphoma, ALK associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma, nodal EBV-positive T and NK-cell lymphoma, and nodal T-follicular helper lymphoma, and primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoid proliferations and lymphomas.
Plasma cell neoplasms and other diseases with paraprotein include many disease entities such as plasma cell myeloma, plasmacytoma, monoclonal gammopathies, immunoglobulin-related amyloidosis, and monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease, etc.
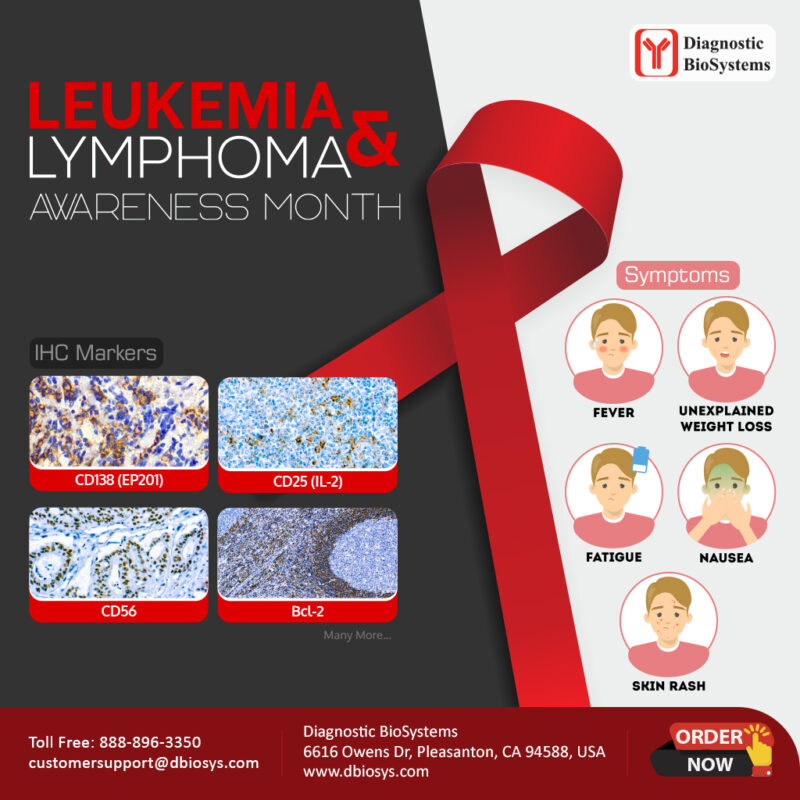
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) plays an important role in the identification, differentiation, and classification of various types of blood cancers. The selection of specific IHC markers depends on the morphological and histological features, and immunophenotypes of the blood cancers. The table below lists the IHC antibodies Diagnostic BioSystems can provide for the identification and classification of blood cancers.
| Antibody Marker | Clinical Utility |
| CD138 (Syndecan-1) | Commonly used as a marker for plasma cells and is useful in the identification of plasma cell neoplasms. |
| CD15 and CD30 | Commonly used as a marker for Reed-Sternberg cells, LP/L&H cells and useful in the identification and differentiation of Hodgkin lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte predominance Hodgkin lymphoma. |
| CD5 and CD23 | Commonly used as a combination of markers for tumor cells and useful in the identification and differentiation of small lymphocytic leukemia/lymphoma from other B-cell small cell lymphoma, such as mantle cell lymphoma and marginal zone B-cell lymphoma. |
| CD25 (IL-2R) | Commonly used as a marker for the identification of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. |
| CD56 (N-CAM) | Commonly used as a marker for natural killer cells and useful in the identification and differentiation of NK/T-cell leukemia/lymphomas. |
| MPO (Myeloperoxidase) | Commonly used for myeloid cells and is useful in the identification and differentiation of acute myeloid leukemia and myeloid sarcoma. |
| TdT (Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase) | Commonly as a marker to identify precursor B-cells and T-cells and very useful in the identification and differentiation of precursor B-cell leukemia/lymphoma and precursor T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. |
| BCL-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2) | Commonly used as a marker for identifying neoplastic follicular cells and useful in the identification and differentiation of mature B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma. |
| Ki-67 | Ki-67 is a marker of cell proliferation and is very useful in assessing the growth fraction of lymphoma/leukemia cells, and determining the aggressiveness of lymphoma and leukemia. |
| ALK (Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase) | Commonly used marker for the identification and differentiation of anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL). |
| CD45 (Leukocyte Common Antigen, LCA) | A marker generally used for identifying white blood cells and very useful in the identification and differentiation of the blood cancers that are originated from hematolymphoid system. |
| CD20 | Commonly used as a marker for mature B-cells and useful in the identification and differentiation of mature B-cell lymphomas. |
| CD10 | Commonly used as a marker for mature B-cells and useful in the identification and differentiation of follicular lymphoma. |
| BCL-6 | Commonly used as a marker for mature B-cells and useful in the identification and differentiation of mature B-cell lymphomas, such as follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. |
| CD3, CD5, CD7 | Commonly used as markers for mature helper T-cells and useful in the identification and differentiation of mature T-cell lymphomas. |
| CD4 | Commonly used as a marker for mature T-cells and useful in the identification and differentiation of mature T-cell lymphomas such as follicular T cell lymphoma. |
| CD8 | Commonly used as a marker for mature T-cells and useful in the identification and differentiation of mature T-cell lymphomas |
| CD21 and CD23 | C histiocytic/dendritic neoplasms. |
| CD68 and CD163 | Commonly used as a marker for mature monocytic cells and useful in the identification and differentiation of monocytic neoplasms. |
| CD61 | Commonly used as a marker for megakaryoblastic cells and useful in the identification and differentiation of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. |
| Kappa and lambda light chain | Commonly used as a marker for monoclonality of mature B-cells and plasma cells to identify neoplastic process and very useful in the identification and differentiation of mature B-cell lymphomas and plasma cell neoplasms. |
| Mast cell tryptase and mast cell chymase | Commonly used as a marker for mast cells and useful in the identification and differentiation of mastocytosis. |
| Amyloid Precursoe protein and beta-Amyloid protein | Commonly used as a marker for Amyloid material and useful in the identification and differentiation of immunoglobulin-related amyloidosis, and monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease. |
| IgA, IGM, and IgG | Commonly useful in the identification and differentiation of monoclonal gammopathies. |
#BloodCancerAwareness #CancerAwarenessMonth #HematologicCancer #CancerResearch