Blog
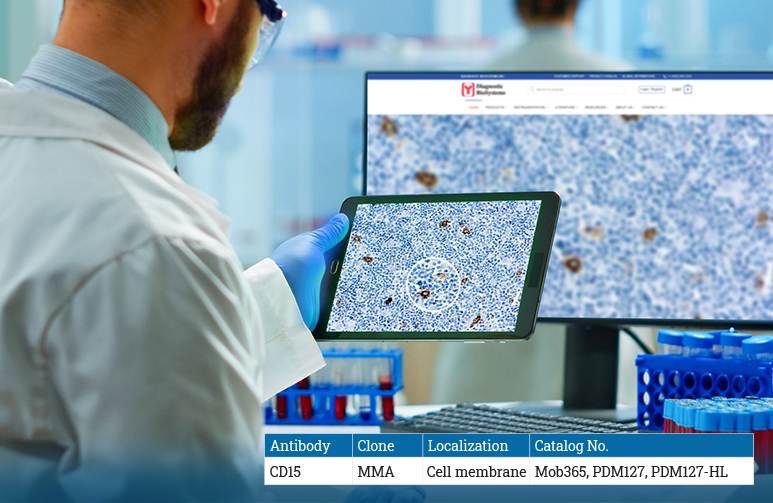
CD15
CD15, also known as LeuM1, is a carbohydrate antigen and anti-CD15 is primarily used in the differential identification of Reed-Sternberg cells and or Hodgkin cells for classic Hodgkin lymphoma (usually positive) and the LP/L&H cells (usually negative) of Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. It shows membranous, Golgi, or diffuse cytoplasmic staining patterns. The large immunoblasts in infectious mononucleosis caused by EBV infection can be binucleated, mimicking Hodgkin/ Reed-Sternberg cells. These cells are usually CD15 negative or rarely weak positive. About 15 % of peripheral T cell lymphoma express CD15. Some acute leukemia, particularly acute myelomonocytic and monocytic leukemia, and granulocytic sarcoma can show CD15 expression with poor prognosis.Approximately 50% of carcinomas, including colorectal carcinoma, ovarian serous carcinoma, and renal cell carcinoma would express CD15. CD15 positivity can also be found in normal tissues and cells, such as myeloid cells, eosinophils, basophiles, granulocytes, kidney proximal convoluted tubules, and small intestine Paneth cells, which can be well utilized as an internal control for IHC staining procedures.