p63
Description
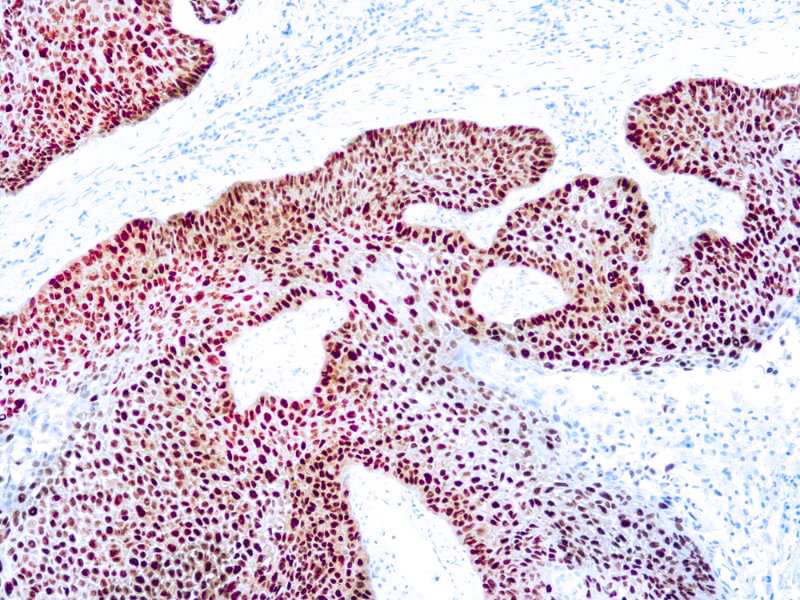
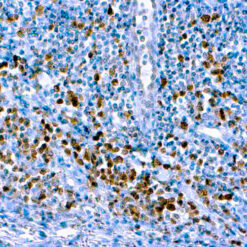
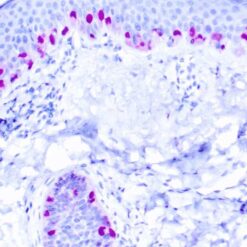
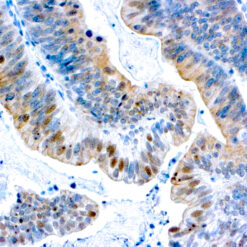
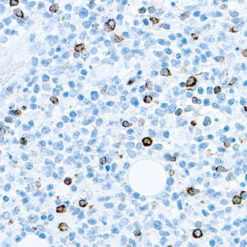
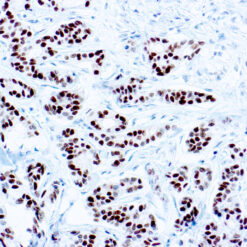
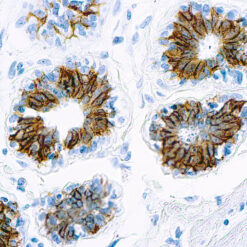
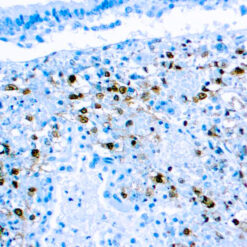
p63 is a homolog of the tumor suppressor p53, it is identified in basal cells in the epithelial layers of a variety of tissues, including epidermis, cervix, urothelium, breast and prostate. p63, vital for the development of the prostate and selectively expressed by normal prostate basal cells, has been shown to be a promising complementary basal cell specific marker to High Molecular Weight-Cytokeratin (HMW-CK), for the differential diagnosis of benign prostatic lesions and prostatic carcinoma. p63 has also been shown to be a sensitive marker for lung squamous cell carcinomas (SqCC), with a sensitivity of ~90% . Specificity for lung SqCC, vs. lung adenocarcinoma (LADC), is approximately 80. In breast tissue, p63 has been identified in myoepithelial cells of normal ducts.
Additional information
| Catalog No. | RMAB086R, RMPD086R |
|---|---|
| Clone | DBR16.1 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Immunogen | Recombinant human p63 protein fragment |
| Species | Rabbit |
| Cellular Localization | Nuclear |
| Positive Control Tissue | Prostate Ca, Tonsil |
| Pretreatment | EDTA Buffer pH 8.0 |
| Incubation & Temperature | 30 min @ RT |
| Intended Use | RUO |
| Detection System | PolyVue Plus – Two Step Detection System or Montage PolyVue Plus Auto Detection System for Montage 360 System |
| Description/Type | Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Format | Purified immunoglobulin |
DATASHEETS & SDS
DATASHEETS & SDS
| Download R Datasheet |
| Download SDS Sheet – OSHA |
REFERENCES
REFERENCES
- Yang A, et al. p63, a p53 homolog at 3q27–29, encodes multiple products with transactivating, death-inducing, and dominant-negative activities. Mol Cell. 1998 Sep; 2(3):305-16.
- Mukhopadhyay S, et al. Subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinomas lacking morphologic differentiation on biopsy specimens: Utility of an immunohistochemical panel containing TTF-1, napsin A, p63, and CK5/6. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011 Jan; 35(1):15-25.
- Tacha D, et al. A six antibody panel for the classification of lung adenocarcinoma versus squamous cell carcinoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2012 May; 20 (3):201-7.
- Terry J, et al. Optimal immunohistochemical markers for distinguishing lung adenocarcinomas from squamous cell carcinomas in small tumor samples. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010 Dec; 34(12):1805-11.
- Pu RT, et al. Utility of WT-1, p63, MOC31, mesothelin, and cytokeratin (K903 and CK5/6) immunostains in differentiating adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and malignant mesothelioma in effusions. Diagn Cytopathol. 2008 Jan; 36(1):20-5.
- Lerwill MF. Current practical applications of diagnostic immunohistochemistry in breast pathology. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004 Aug; 28(8):1076-91
Reviews (0)
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.